Types of Restrictions on Free Trade – Economics Revision – The Tutor Academy
Types of Restrictions on Free Trade – Economics Revision – The Tutor Academy
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Types of Restrictions on Free Trade
Quotas
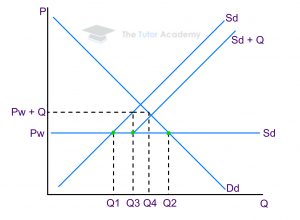
Quotas are limits on the quantity of a product being imported. It restricts the physical amount of product which a country can buy
Q1 – domestic supply at price pw
Q2 – domestic demand at price pw
An import quota is put in place by the government government; this is shown at Q3
Before quota the difference between Q2 and Q1 was the number of imports coming into the country
After the quota there is a fall in the number of imports allowed into the country, Q1 to Q3 is the new level of imports allowed.
This leaves an excess demand of Q2 to Q3. As a result of this there is pressure applied to the price and so the market pushes up the price to Pw+Q
At the new price, new suppliers enter market as they are incentivised by the higher price This leads to increase in supply from Sd to Sd+Q
Domestic suppliers now supply up to Q4
This results in a contraction of demand.
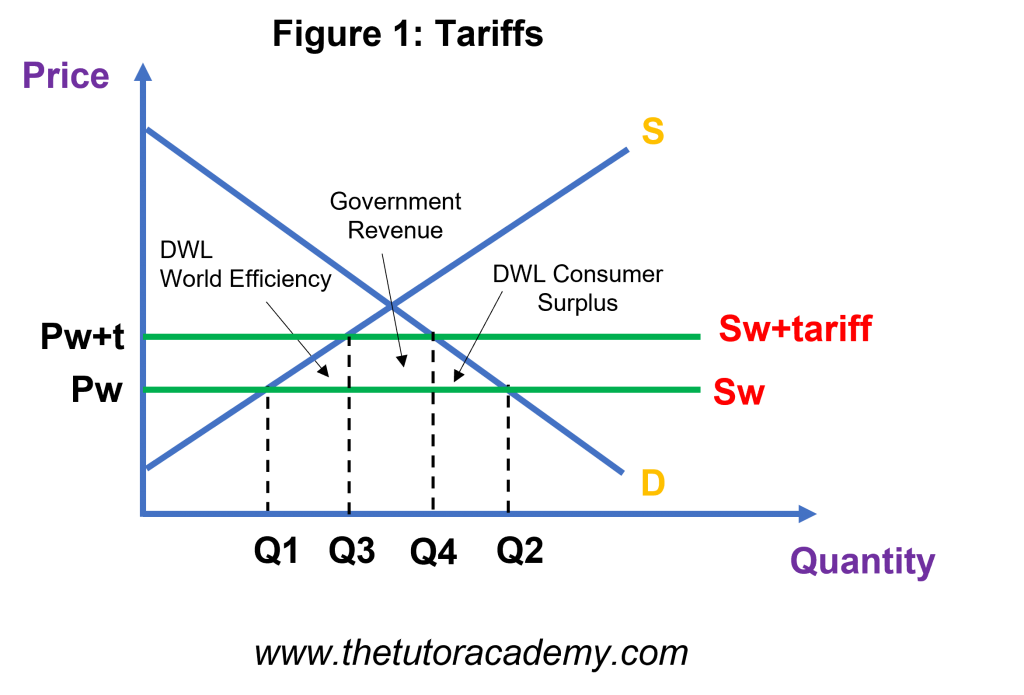
Tariffs
Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods. The aim of tariffs is to increase the price of a product and discourage a country to import more
Subsidies
[diagram]
Firms are offered subsidies from the government to encourage them to lower their costs and become more competitive.
Subsidies reduce the price a firm pays for each unit and consumer also pay less as the products are subsidised by the government
Non-tariff Barriers
Some other methods to reduce free trade include: the health and safety regulations imposed, labelling of products and environmental regulation
The impact of Protectionist Policies
- Producers – firms face less competition and can produce lower average costs
- Consumers – restrictions such as Tariffs and Quotas raise the price of the imported products, hence consumers are left with less choice and variety
- Government – the government is able to increase their tax revenue generate through import taxes and tariffs
- Economy – lower output is caused because of less specialisation and a depletion of the country’s comparative advantage
Quick Fire Questions – Knowledge Check
1. Identify and explain four types of Restrictions on Free Trade (8 marks)
2. Using a diagram, explain the effect of a tariff and how it acts as a barrier for trade (4 marks)
3. Using a diagram, explain the effect of a subsidy and how it acts as a barrier for trade (4 marks)
4. Explain the impact of Protectionist Policies (8 marks)
Next Revision Topics
- Restrictions on Free Trade
- Patterns of Trade
- Terms of Trade
- World Trade Organisation
- Specialisation and Trade
- Globalisation
- Imports / Exports
- Balance of Payments
- Exchange Rates
- International Competitiveness
- Trading Blocs
Level Economics Past Papers