Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum – Theory
Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum – Theory
Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum – Theory
Understanding management, leadership and decision-making
The Tannenbaum and Schmidt Continuum theory highlights the relationship between the different levels of freedom that a manager chooses to give to his employees and the level of authority he decides to use when managing his staff.
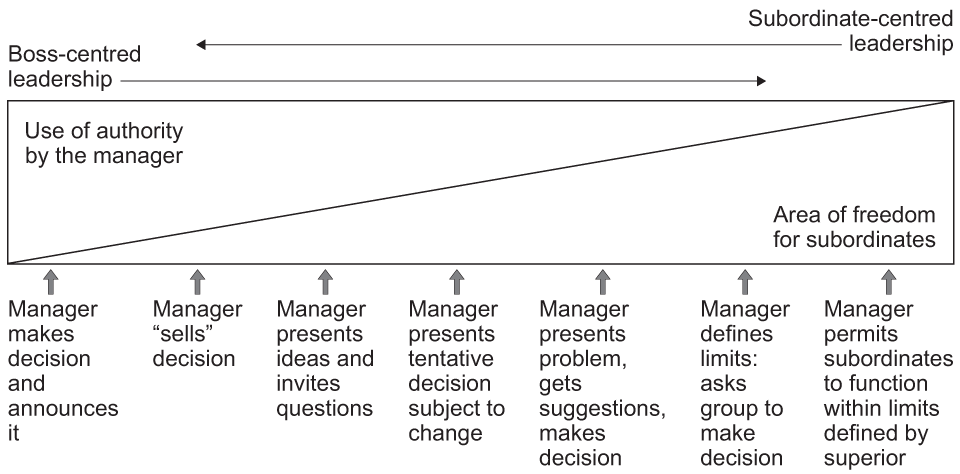
Source: aqa.org.uk
When to use this theory?
This theory is best used when discussing the influences on and impact of different management and leadership styles.
Leadership Styles
The four main leadership styles are highlighted below:
1. Authoritarian
Authoritarian leaders hold onto as much power and decision making as possible. There is very little delegation and the power is from top management to workers at the bottom of the chain. This is usually used when workers are unskilled.
2. Paternalistic
The leader decides what is best for his employees with very little delegation.
This is a softer form of authoritarian leadership, which often leads to better employee motivation, morale and lower staff turnover. A paternalistic leader is likely to explain his actions to his employees more than an authoritarian leader.
3. Democratic
Decision making is shared with the group rather than only being made by management. This leadership style allows employees to become more empowered as they are being involved in the decision-making process. This is becoming the most popular leadership style over time. It’s proving to be more effective with the management of skilled and experienced labour workers.
4. Laissez-faire
Laissez-faire leadership style means to “leave alone”. Leadership has little input into the day-to-day decision-making as it is delegated throughout the entire team. This can be an effective management style if workers are motivated and can be trusted to complete their jobs to a high standard.
