Supply (AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL)
Supply (AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL)
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Supply
Definition
Supply is the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing to supply at a given price.
Supply curve
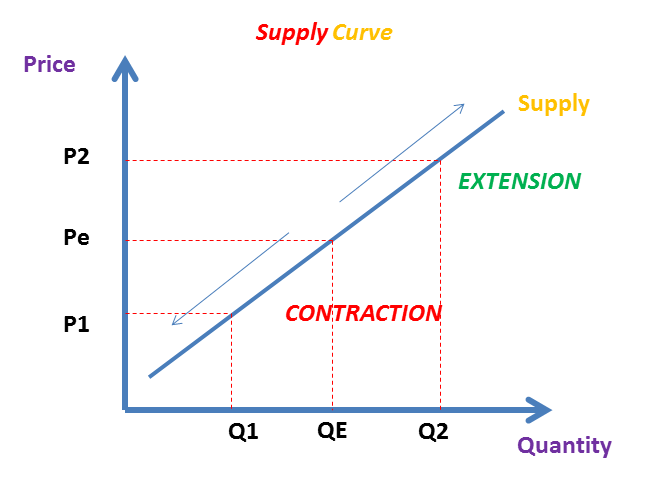
The supply curve shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Why is the supply curve upward sloping?
The supply curve is upward sloping from bottom left to top right for the following reasons.
- The higher the price the more quantity that is supplied by the producer. As the price increases this provides an incentive for producers to supply more as they can earn higher profits.
- As a firm increases output and expands, its cost of production will also increase. This firm needs to cover these higher costs by increasing prices.
What causes a movement along the supply curve?
There is a movement along the supply curve only when there is a change in price.
Extension vs contraction of the supply curve
An increase in price causes an extension in supply. A fall in price causes a contraction in supply.
Shifts in the supply curve
Shifts in the supply curve are caused by any other factor other than a change in price.
Causes of shifts in the supply curve
- Changes in the price of substitutes
If the price of one substitute increases such as butter. Firms could find more people demanding margarine as a viable alternative. This would lead to an increase in the supply of margarine.
- Indirect tax changes e.g. VAT
An increase in VAT could lead to decreased demand for a product. This would lead to a decrease in supply.
- Subsidies provided by the government or other agencies
A subsidy will decrease the cost of production and reduce the price. This will therefore encourage producers to increase supply.
- Improvements in technology
The introduction of more efficient technology could help increase supply.
- Changes in weather
Weather can positively or negatively impact the supply of certain products. The supply of ice creams generally increases during the summer due to good weather.
- Changes in the cost of production e.g. wages or raw materials
A decrease in the cost of production will lead to firms being able to supply more. E.g. if firms have to pay less wages they can use the money saved to produce more.
OCR Spec – Additional Content
Types of Supply
Joint Supply
When the increase in the supply of one good will lead to an increase or decrease in the supply of another good. For e.g. a larger supply of cows will increase the supply of milk
Composite Supply
This is when the good /service can be acquired from several different sources
Competitive Supply
The raw materials used to produce the good are in competition with each other and are perfect substitutes
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
- Define supply (2 marks)
- Explain why the supply curve is upward sloping from left to right (4 marks)
- Explain what a contraction and extension is in supply (4 marks)
- Explain what causes a movement in the supply curve (4 marks)
- Explain what causes shifts in the supply curve, by providing 5 examples (6 marks)
Next Topics:
- Demand
- Market Equilibrium
- Subsidy
- PES
- Supply Side Policies
- Aggregate Supply
A Level Economics Past Papers