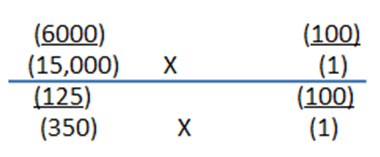Price Elasticity of Supply – PES (AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL)
Price Elasticity of Supply – PES (AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL)
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Price Elasticity of Supply – PES
Price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of supply to a change in price.
Simple explanation
What happens to the quantity supplied of a product when the price changes.
If the price of a Playstation 4 increased from £350 to £450. This would provide an incentive for firms to supply more of the product. This would lead to an increase in the quantity supplied from 500 units to 800 units.
PES Formula
PES = % change in quantity supplied / % change in price
Worked Example of PES:
Sony PlayStation
Exam Tip: Key to working out PES
Step 1
Step 2
Types of price elasticity of supply
If PES > 1 = The good is price elastic
This means that the percentage change in supply will be higher than the percentage change in price.
If PES < 1 = The good is price inelastic
This means that the percentage change in supply will be lower than the percentage change in price.
If PES is = 1 The good is Unit Elastic
This is when the percentage change in supply is the same as the percentage change in price. A 20% decrease in the price of strawberries may cause a 20% increase in the supply of strawberries.
If PES is = 0 The good is perfectly inelastic
This is when the change in price will not affect the supply of the product. The supply curve will be vertical.
If PES is = Infinity The good is perfectly elastic
The supply curve will be horizontal.
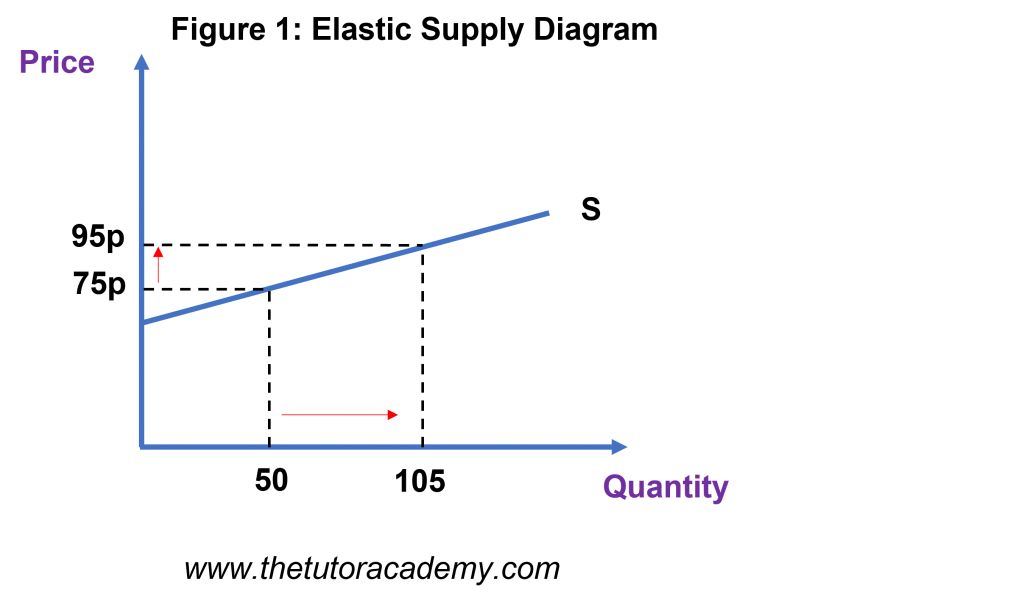
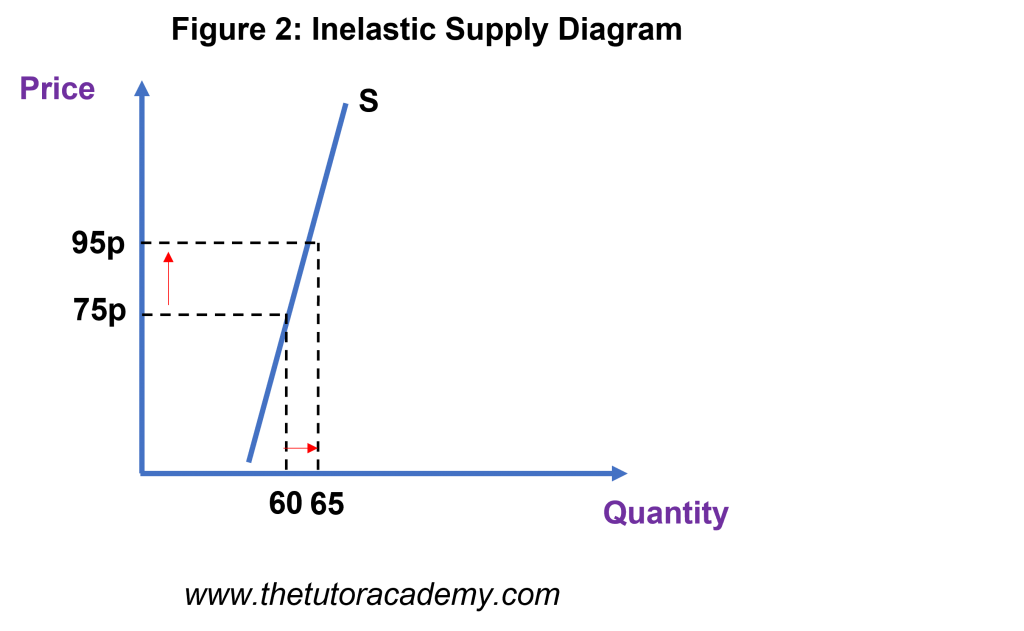
PES Diagrams
Elastic
Inelastic
Factors influencing Price Elasticity of Supply
Time
- In the Short Run, at least one factor of production is fixed, hence the elasticity of supply is likely to be inelastic
- In the Long Run, all factors of production can be varied, hence the elasticity of supply is likely to be elastic
Stocks
- The supply will be elastic if there are stocks of finished goods available as manufacturers can respond quickly to a price change
Availability / cost of switching from one factor of production to another
- Supply will be elastic if it is easier and cheaper to switch from one factor of production to another. e.g if labour or machinery can be used to multiple parts of the process, supply is likely to be elastic
Spare Capacity
- Supply is likely to be elastic if factors of production have been under-utilised or underemployed
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
1. Define PES (2 marks)
2. State the formula for PES (2 marks)
3. Explain what the following suggest (4 marks)
- a) PES > 1
- b) PES <1
- c) PES = 1
- d) PES = Infinitiy
4. If the price of a cappuccino increases by 10%, and the supply increases by 20%. Calculate the price elasticity of supply (4 marks)
5. Draw a PES diagram showing the following (4 marks)
- Elastic
- Inelastic
- Perfectly elastic
- Perfectly inelastic
- Unit elastic
6. Explain four factors influencing the Price Elasticity of Supply (8 marks)
Next Revision Topics:
- Supply
- Demand
- Market Equilibrium
- Price Elasticity of Demand
- Income Elasticity of Demand
- Cross Elasticity of Demand
A Level Economics Past Papers