Perfect Competition – Economics Revision – The Tutor Academy LTD
Perfect Competition – Economics Revision – The Tutor Academy LTD
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Perfect Competition
Perfect competition occurs in markets where there are many small firms and low barriers to entry.
Examples of perfect competition
Newsagents – Local independent newsagents normally sell the same confectionery and newspapers.
Agricultural markets – A farmers market will be selling the same selection of Fruit and Veg.
Characteristics of Perfect Competition
- Many small firms
- Low barriers to entry
- Homogenous products (Identical)
- Perfect knowledge
- Price takers
Perfect Competition – Diagrams
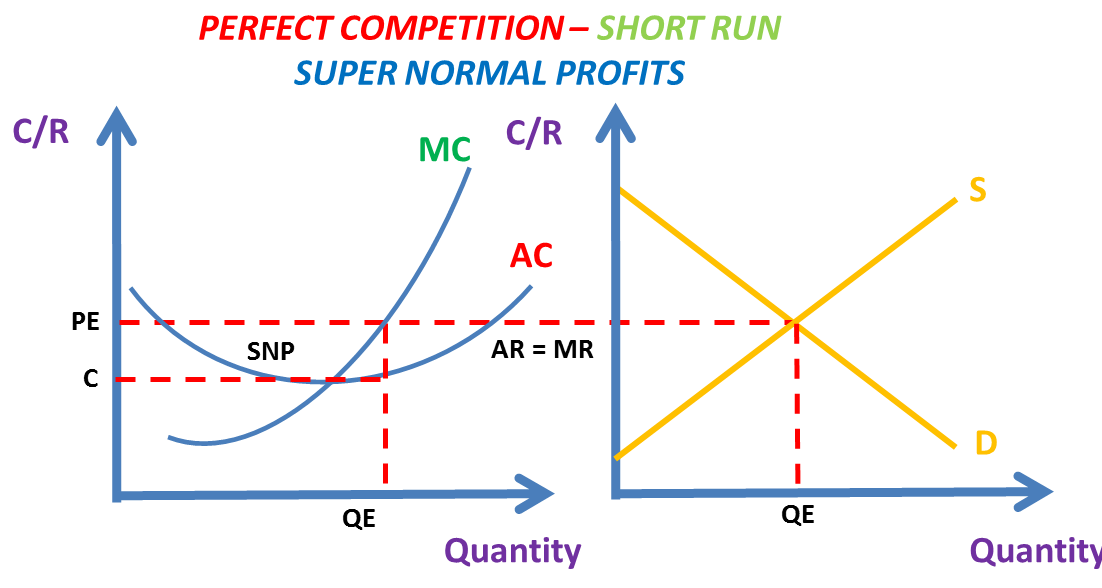
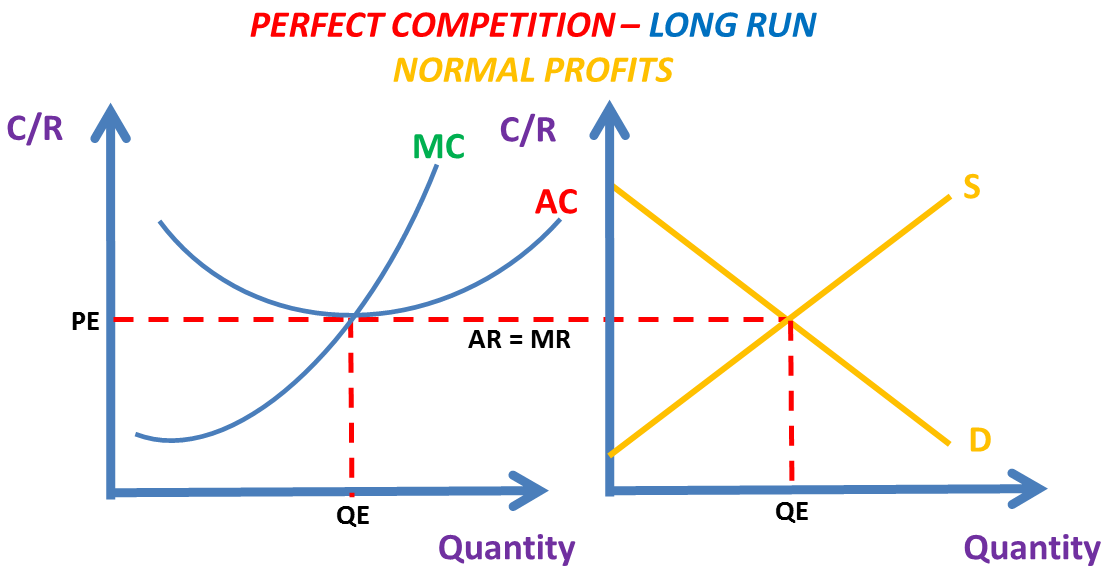
- A perfectly competitive firm will make supernormal profits in the short run and normal profits in the long run.
- Firms under perfectly competitive markets aim to profit maximise at MC = MR.
- Perfectly competitive firms are also price takers and therefore have a horizontal demand curve (AR & MR).
- Initially the newsagent will be the only firm in the market or local area. This will allow the firm to make supernormal profits in the short run due to a lack of competition.
- However in the long run other entrepreneurs will be attracted by this firms profits. Also due to the low barriers to entry new firms will enter the market increasing the number of firms. This would cause the supply curve to shift right and lower the price level.
- It’s clear to see the AR = MR curve is lower in the long run diagram than the short run diagram. The P = AR = MR curve is at the bottom of th AC curve in the long run. However the P = AR = MR was above the AC curve in the short run diagram.
- Supernornal profits will now be competed away between all the firms in this market. They will all therefore be making normal profits in the long run.
- New firms were easily able to enter due to the low barriers to entry, perfect knowledge of how firms operate in this market and due to the products being identical.
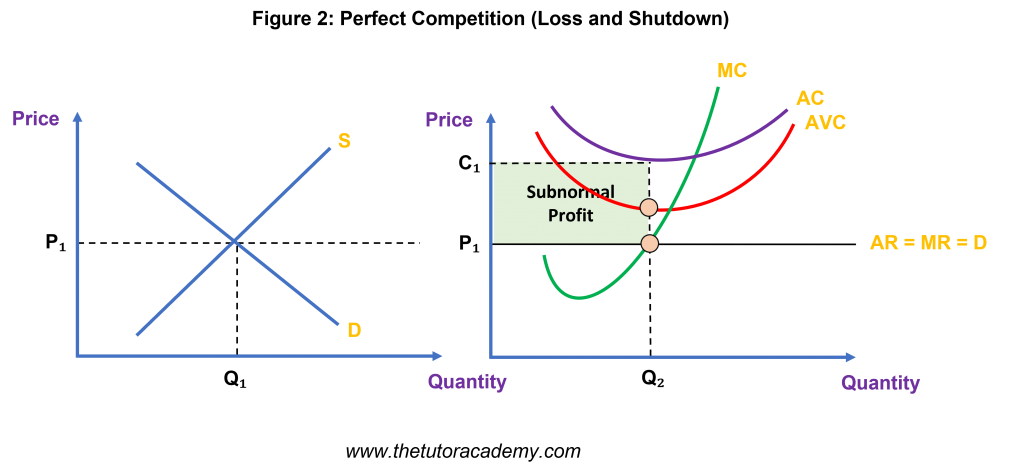
This firm will make a loss but will not shut down as the Average Revenue is still greater than the Average Variable Cost. This firm will stay open, making a loss, as long as it can cover it Average Variable Cost.
This firm will shut down as the average revenue is less than the average variable costs. (AR < AVC)
Advantages of Perfect Competition
- In the long run, firms produce at P=MC, so there are lower prices and allocative efficiency
- In the short run, firms generate supernormal profit which can increase dynamic efficiency through investment
- Firms also operate at the lowest point on the AC curve, suggesting they are productively effiicient
Disadvantages of Perfect Competition
- In the long run, firms struggle to make supernormal profits, making it harder to by dynamically efficient
- Firms hardly benefit from economies of scale since they are small in size
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
1. State all the characteristics of a Perfect Competition market structure (4 marks)
2. Explain what type of profit a perfectly competitive market makes in the short run and in the long run (4 marks)
3. Explain why the AR and MR curve is horizontal (3 marks)
4. Identify what else the AR and MR known as (2 marks)
5. Draw a short run and long run diagram with the market diagram on the right (6 marks)
6. Draw a short run perfect competition diagram by itself (3 marks)
7. Draw a long run perfect competition diagram by itself (3 marks)
8. State at which point a perfectly competitive firm produces at (2 marks)
9. Discuss whether a perfectly competitive firm is allocatively and productively efficient in the short run and long run (4 marks)
Next Revision Topics:
A Level Economics Past Papers