Market Structures – AQA Spec
Market Structures – AQA Spec
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
What is a Market Structure?
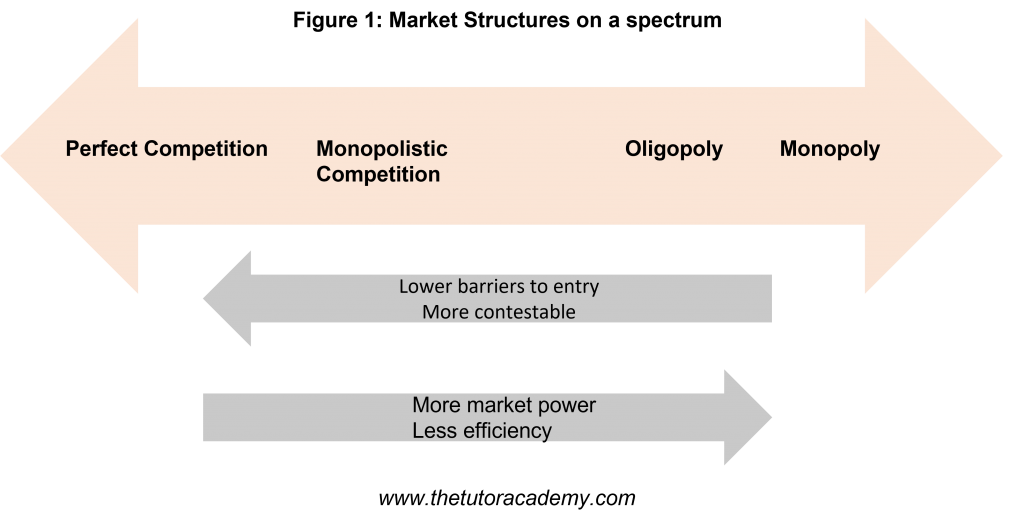
The Market Structure refers to how the market is organised; there are four market structures:
Each Market Structure is characterised by:
The number of firms in the market
A market is more competitive when they are more firms in it
The degree of product differentiation
A market is less competitive if the products are more differentiated. In a perfectly competitive market, products are homogenous and have no product differentiation
Product differentiation can occur through price, branding, and quality
Ease of entry into the market
This refers to the number and types of barriers to entry
The market becomes less competitive if there are higher barriers to entry as producer surplus rises
Barriers to entry can be strategic (limit pricing or predatory pricing), structural (differences in production costs), or statutory (patents protect a franchise)
Next Revision Topics:
A Level Economics Past Papers