Government Spending – AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL
Government Spending – AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Government Spending
Government spending is a component of aggregate demand (AD).
AD = C + I + G + (X – M)
C = Consumption (Around 60% of AD is consumption)
I = Investment
G = Government Spending
X = Exports
M = Imports
The Main Influences on Government Expenditure
Governments can decide on what and where to spend their money. Most governments also try to stick to a planned budget to ensure they do not create a large deficit (debt).
Fiscal Policy
Government spending can help to stimulate growth in the economy through a positive multiplier with the use of expansionary fiscal policy (Government spending & Taxation).
Governments are also responsible for spending on key areas of the economy e.g.
- Health
- Education
- Infrastructure
- Defence
The amount of government spending also depends on the amount of taxes the government collects e.g. income tax, VAT, corporation tax etc.
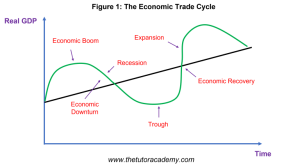
Trade Cycle
The Trade Cycle shows how a country can experience fluctuations in its economic growth depending on different phases and how the levels of government spending vary according to the stage of the Trade Cycle
The Characteristics of a Boom
A Boom is a period where countries experience high Economic Growth
- High Employment – firms are able to hire more workers and invest into employee training
- Increased Investment – consumers are able to invest more money into bonds / stocks / shares and firms are able to expand their investment into capital / technology / R&D
- Increased Living Standards – people experience a higher standard of living and quality of life
- Inflation – higher inflation is likely to occur if there is great economic growth and more consumers spending money on goods / services. Demand-Pull Inflation and Cost-Push Inflations will occur
The Characteristics of a Recession
A Recession is a period where there is a significant decline in Real GDP and Economic Growth
- Lack of Investment – firms and consumers do not have enough money to invest into other resources
- More Unemployment – in order to keep costs low, firms may restrict the number of employees they can hire or fire existing workers
- Currency Instability – exchange rates may rise or a country could be faced with a fixed exchange rate system
- Lack of International Trade – countries may not have enough funds to trade with other countries, affecting its competitiveness. There may also be high tariffs and other forms of protectionism in place
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
1. Explain how the Fiscal Policy influences levels of Government Expenditure (4 marks)
2. Explain how the Trade Cycle influences levels of Government Expenditure (8 marks)
Next Revision Topics
- Aggregate Demand
- Economic Growth
- Indirect & Direct Taxes
- Fiscal Policy
- Investment
- Consumption
- Exports / Imports
- The Trade Cycle
A Level Economics Past Papers