Elements, compounds and mixtures
Elements, compounds and mixtures
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Chemistry Revision Notes
Elements
Elements are made up of only one type of atom. Each atom in an element must have the same atomic number.
All the elements on earth can be found in the periodic table.
C = Carbon F= Fluorine Na = Sodium K = Potassium
Isotopes
An Isotope is an element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. The atomic number will be the same but the mass number will be different.
E.g. Hydrogen has 1 proton and 1 electron. It also has two other isotopes.
Image source: Pixabay
| Isotope | Protons | Electrons | Neutrons |
| Protium (Hydrogen) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Deuterium | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Tritium | 1 | 1 | 2 |
To calculate the relative atomic mass of an element:
relative atomic mass (Ar) = sum of (isotope abundance × isotope mass number)
sum of abundances of all isotopes
Compounds
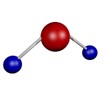
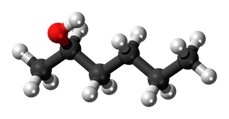
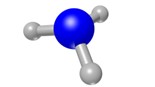
A compound is when two or more different types of atoms are chemically joined together.
e.g.
Water Hexanol Ammonia
Image source: Pixabay
Molecules
A molecule is when more than two atoms are chemically joined together. A molecule can be an element or a compound.
e.g. H2O is a molecule and a compound. N2 is a molecule and an element.
Formulae
In order to represent a molecule, chemical formulae are used. The subscript number represents the number of atoms (when there is more than one) that are present in that molecule.
e.g. Carbon dioxide has one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
Mixtures
A mixture is where there are two or more substances (elements or compounds) mixed together but not chemically bonded together. Mixtures are easy to separate. E.g. air and salt-water.
Separating mixtures
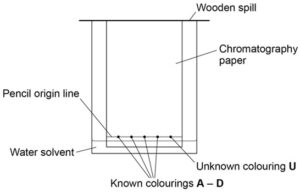
Chromatography
Paper chromatography can be used to separate mixtures of soluble substances. The mixture is often a coloured substance such as food colourings, inks, dyes or plant pigments.
Chromatography is often used to find an unknown compound by comparing it to a known set of compounds.
E.g. Finding an unknown food colouring
Image source: AQA required practical handbook
Chromatography involves two different ‘phases’:
- The stationary phase which is the chromatography paper (it does not move).
- The mobile phase which is the solvent that moves through the paper, carrying the dissolved substances with it.
Rf Values
An R f value is calculated and used to identify unknown chemicals. The Rf value of a compound can be compared to the Rf value of a range of reference substances.
Rf = distance travelled by substance
distance travelled by solvent
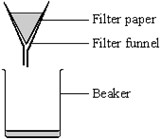
Filtration
Filtration is used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid. It uses filter paper to catch the solid (residue).
Source: AQA exam paper
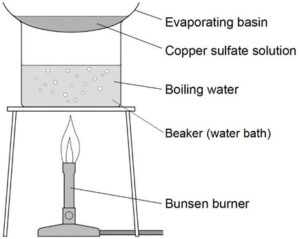
Evaporation and crystallisation
Evaporation is used to separate a soluble salt from a liquid. The solution is heated until the liquid evaporates and the solid is left behind.
Crystallisation is a slower method to separate a soluble salt from a liquid.
The solution is heated in order to make it concentrated and when crystals begin to form, the heating is stopped. The evaporating basin is then left to evaporate at room temperature and crystals will form slowly. This method can be used to make copper sulphate crystals.
Source: AQA required practical handbook
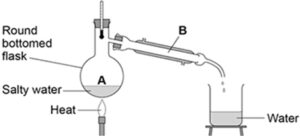
Distillation
Simple distillation is used to separate a liquid from a solution. The process involves evaporating the liquid from the solution and then condensing it.
Source: AQA exam paper
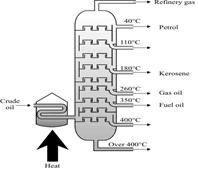
Fractional distillation is used to separate out a mixture of liquids. It is used to separate out crude oil into fractions.
The process involves evaporating the different liquids at their different boiling points and then condensing them and collecting them.
Source: AQA exam paper
Questions
- A substance in which atoms of two or more different elements are chemically combined are called _____________________ .
- What is an element?