Consumer & Producer Surplus (AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL)
Consumer & Producer Surplus (AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL)
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Consumer Surplus
Definition
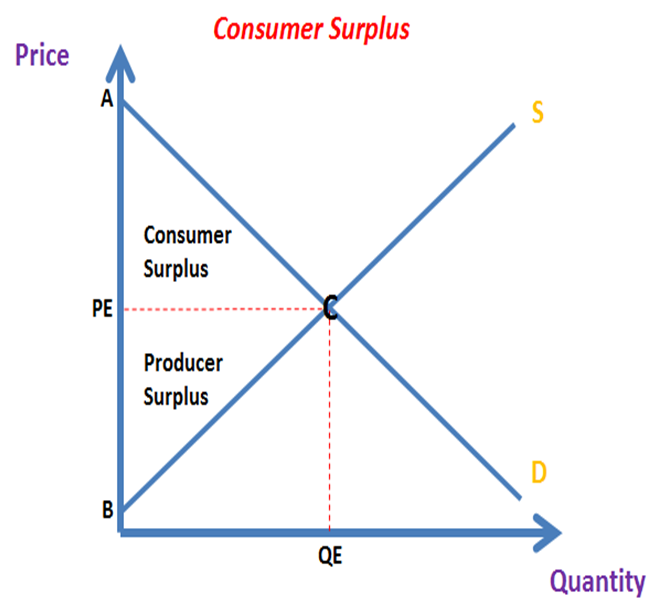
Consumer surplus represents the difference between the price a consumer is paying for a good and the highest price he is willing to pay.
Producer Surplus
Definition
Producer surplus represents the difference between the price a producer receives for a good and the lowest price he is willing to accept.
Consumer Surplus + Producer Surplus equals the total benefit that society gains from any economic transaction
Consumer & Producer Surplus Areas:
Consumer surplus = PE, A, C
Producer surplus = PE, B, C
Consumer & Producer Surplus – Impact of shifts
A reduction in advertising by a firm could lead to a decrease in demand for a firms products from D to D1. This would cause a change in consumer and producer surplus.
What’s the Impact of a demand shift to the left on consumer and producer surplus?
- Original Consumer Surplus = PE,Q,R
- New Consumer Surplus = P1, S, U
- Change in consumer surplus = PE,Q,R – P1, S, U
- Original producer surplus = PE, Q, T
- New producer surplus = P1, S, T
- Change in producer surplus = PE, P1, S, Q
A government subsidy to a firm would cause the supply curve to shift to the right. This would cause a change in consumer and producer surplus.
What’s the Impact of a supply shift to the right on consumer and producer surplus?
- Original consumer surplus = PE, A, E
- New consumer surplus = P1, A, C
- Change in consumer surplus = PE, P1, C, E
- Original producer surplus = PE, E, D
- New producer surplus = P1, C, B
- Change in producer surplus = PE, E, D – P1, C, B
AQA Spec – Additional Content
Price Discrimination and Deadweight Loss with monopoly
- Firms can maximise their profits and producer surplus by charging consumers with different prices
- When the equilibrium price and quantity are not equal, deadweight loss arises through a loss of economic efficiency
- Monopolies which produce at the profit maximising level of output will cause society to face a deadweight loss
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
1. Define consumer surplus (2 marks)
2. Define producer surplus (2 marks)
3. Draw a diagram for consumer and producer surplus (4 marks)
4. Draw a CS & PS diagram showing a leftward shift in the supply curve (6 marks)
- Which area is CS?
- Which area is PS?
- New PS?
- New CS?
- Change in CS?
- Change in PS?
6. Draw a CS & PS diagram showing a rightward shift in the demand curve (6 marks)
- Which area is CS?
- Which area is PS?
- New PS?
- New CS?
- Change in CS?
- Change in PS?
Next Revision Topics:
A Level Economics Past Papers