Trade Cycle
Trade Cycle
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Trade Cycle
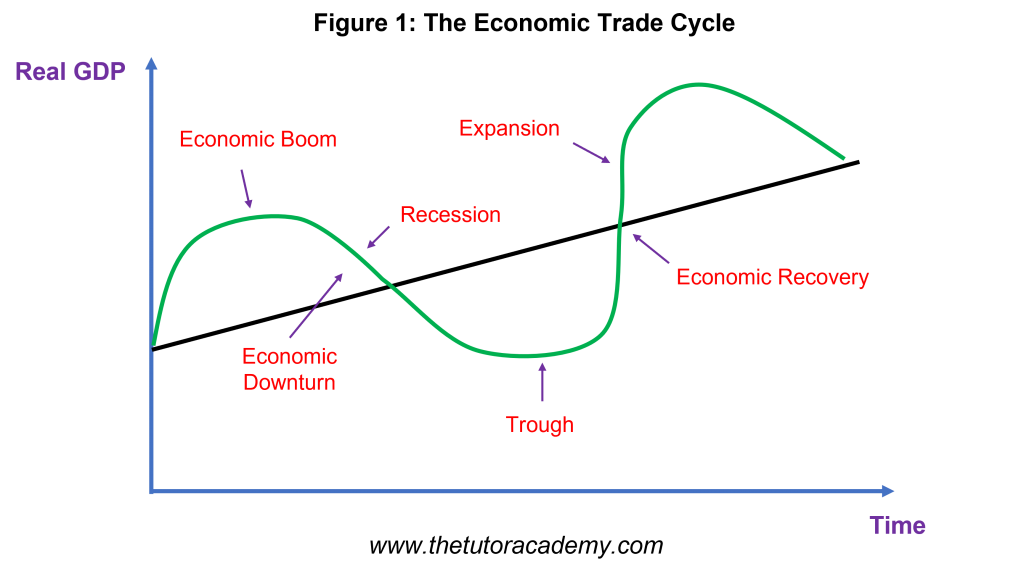
The Trade Cycle shows how a country can experience fluctuations in its economic growth depending on different phases
The Characteristics of a Boom
A Boom is a period where countries experience high Economic Growth
- High Employment – firms are able to hire more workers and invest into employee training
- Increased Investment – consumers are able to invest more money into bonds / stocks / shares and firms are able to expand their investment into capital / technology / R&D
- Increased Living Standards – people experience a higher standard of living and quality of life
- Inflation – higher inflation is likely to occur if there is great economic growth and more consumers spending money on goods / services. Demand-Pull Inflation and Cost-Push Inflations will occur
The Characteristics of a Recession 
A Recession is a period where there is a significant decline in Real GDP and Economic Growth
- Lack of Investment – firms and consumers do not have enough money to invest into other resources
- More Unemployment – in order to keep costs low, firms may restrict the number of employees they can hire or fire existing workers
- Currency Instability – exchange rates may rise or a country could be faced with a fixed exchange rate system
- Lack of International Trade – countries may not have enough funds to trade with other countries, affecting its competitiveness. There may also be high tariffs and other forms of protectionism in place
Causes of an Economic Trade Cycle
- Momentum Effect – positive economic growth will cause a rise in consumer / business confidence, an increase in asset prices and an accelerator effect in investment. This will potentially result in the country experiencing a ‘Boom’
- Technology – Improvements in technology and innovation will promote economic growth
- Interest Rates – An increase in interest rates is likely to be caused because of high inflation and economic growth. However, higher interest rates will leave households with less disposable income, leading to negative economic growth
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
1. Define a ‘Trade Cycle’ (2 marks)
2. Identify and explain four characteristics of a Boom (8 marks)
3. Identify and explain four characteristics of a Recession (8 marks)
4. Identify and explain three causes of an Economic Trade Cycle (6 marks)
Next Revision Topics
- Economic Growth
- Aggregate Demand
- Aggregate Supply
- Exports / Imports
- Equilibrium Levels of Real National Output
- Circular Flow of Income
- Gross National Income
- Output Gaps
- The Multiplier
A Level Economics Past Papers