Business Objectives
Business Objectives
Business Objectives
The three main Business Objectives are:
- Revenue Maximisation
- Profit Maximisation
- Sales Maxmisastion
The traditional theory is based upon the idea that firms aim to maximise profits. However, firms have other aims too
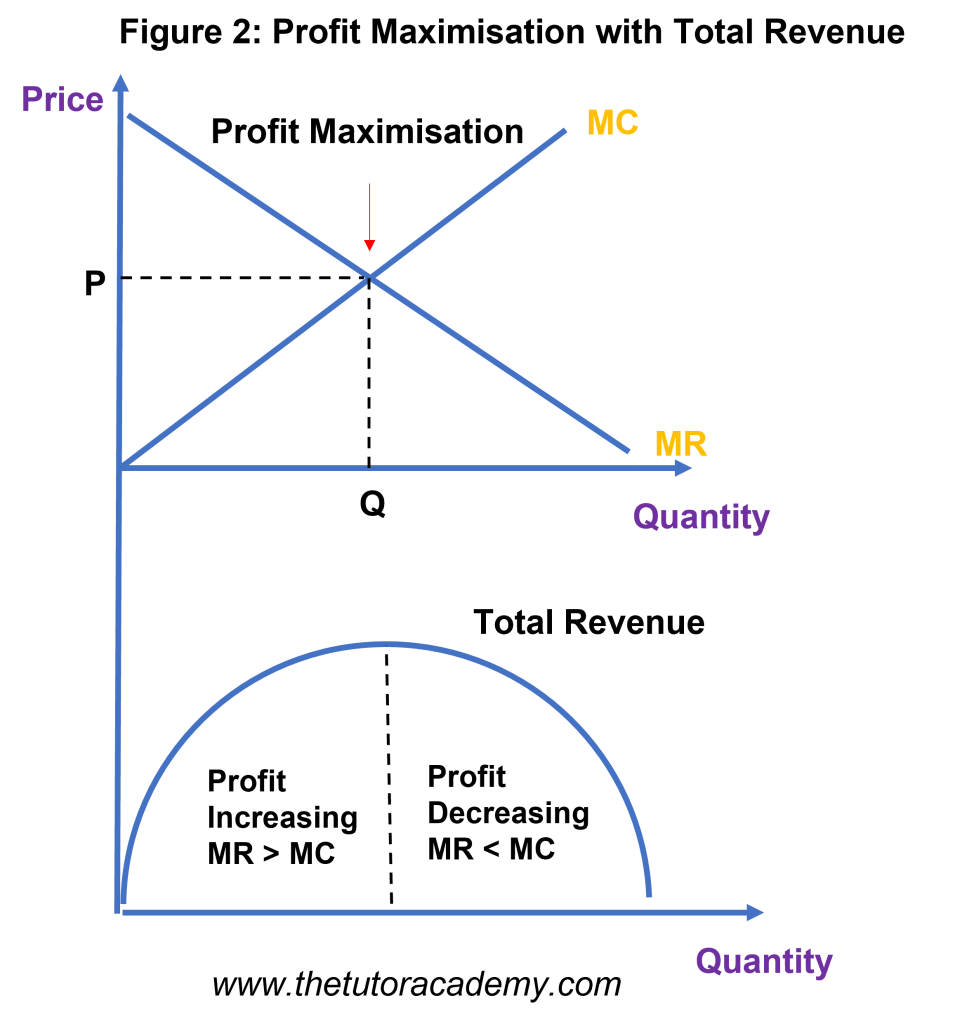
Profit Maximisation
Firms profit maximise at the point MR = MC, where the marginal revenue of selling one extra unit is equal to the marginal cost of producing one more unit
Marginal Profit must also equal zero for firms to profit maximise
Firms break even when total revenue = total cost
Advantages of Profit Maximisation
- Greater investment into R&D – if firms are able to generate more profit, they have more available for investment into new capital/technology, R&D, and innovation
- Greater choice for consumers – if firms have invested into new technology or innovation, they may be able to offer consumers a wider range of goods / services
- Better quality products – more profit made by a firm allows them to implement better production methods and they can provide consumers with higher quality products / services
- Higher wages – Larger profits can be used to pay workers higher wages
- Less chance of a takeover or liquidation occurring – Higher levels of profit generated will make firms less prone to takeover or being liquidated during an economic downturn
- Dividends – Shareholders can benefit from greater dividends
Disadvantages of Profit Maximisation
- Increased competition – Higher profits may incentivise other firms to enter the market, thus increasing competition and reducing market share
- Higher prices – Firms may charge consumers with higher prices
- Lack of ESG policies – There may be a depletion in ethical, social and environmental policies as a result of profit maximisation being the main business objective
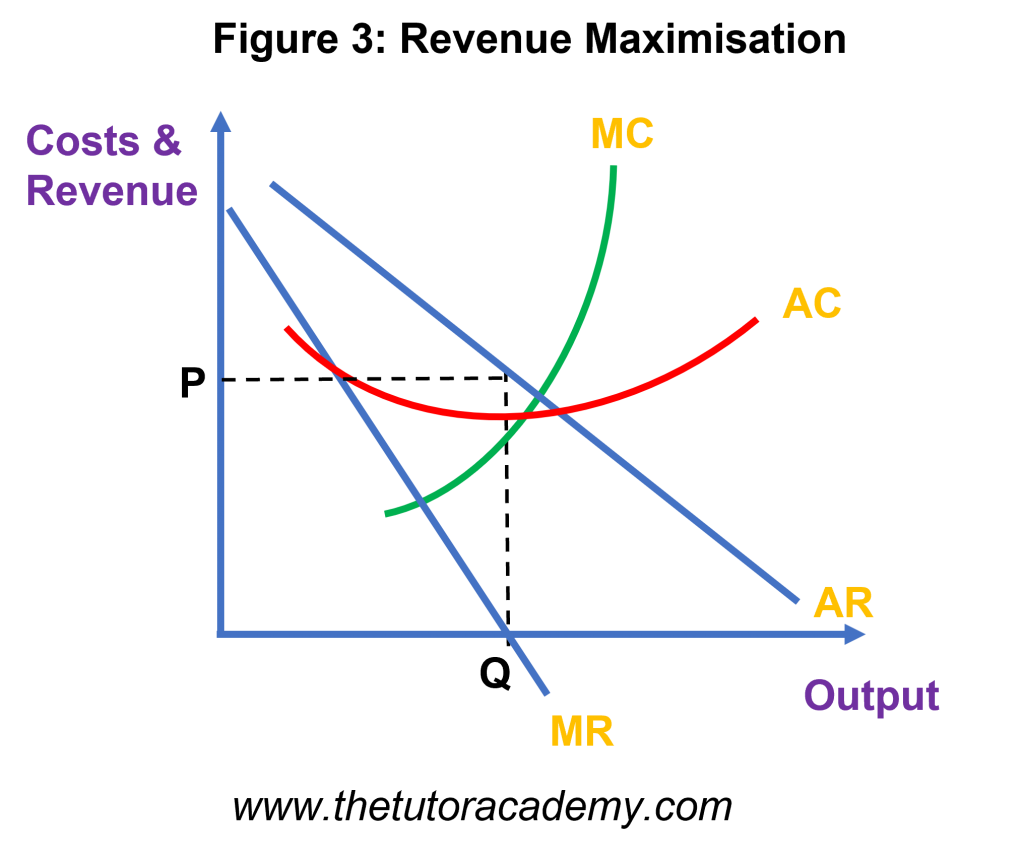
Revenue Maximisation
Revenue Maximisation occurs when firms want to achieve the most amount of sales revenue from selling a larger amount of their products at a lower price
- Firms aim to produce at MR=0, which is the point at which the extra revenue generated from selling another unit equates to the current reduced price on the selling item
Advantages of Revenue Maximisation
- Economies of Scale – Firms can benefit from Economies of Scale and also push out smaller rival firms in the market
- Brand Loyalty – offering lower prices to customers will help retain them and firms will stand out in the market, hence increasing its brand loyalty
- Increased Profitability – firms gain larger market share and benefit from greater economies of scale which mean that they may be able to increase their prices in the future, leading to more profit
Disadvantages of Revenue Maximisation
- Businesses may collapse – If this sustains as the main business objective for a long period of time, firms may suffer a collapse due to potential lack of profit being generated
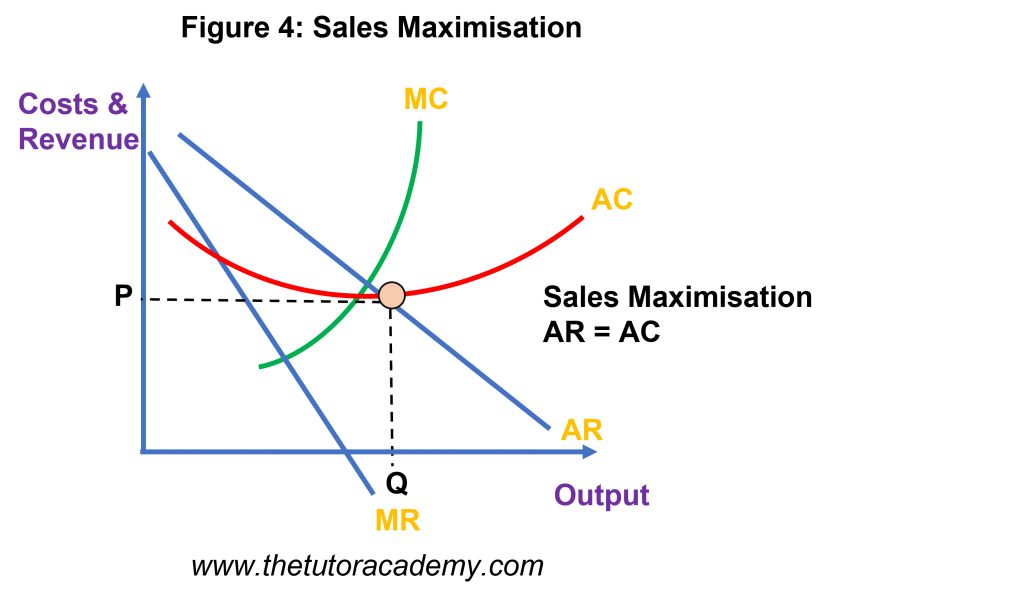
Sales Maximisation
Sales Maximisation occurs when a firm aims to sell as much of a product / service as possible, ensuring a loss is not made
- Occurs at the point AC = AR
Advantages of Sales Maximisation
- Less competition – Lower prices reduce competition and deters other firms from entering the market
- Increased market share – encourage smaller rival firms to be pushed out the market, increasing the firm’s monopoly power – this allows them to charge higher prices to consumers and potentially generate more profit in the long-run
- More consumers – May suggest a larger customer and client base due to more products / services being sold
Disadvantages on Sales Maximisation
- May not be beneficial in the long run – More sales may not necessarily lead to higher income
- Doesn’t necessarily retain consumers – If firms increase their prices, there is no guarantee that customers will continue to buy the product / serviced, regardless of the quantity available
Satisficing
Satisficing is when a firm generates enough profit allowing managers to aim for other business objectives and ensure shareholders are kept happy. Instead of aiming for an optimal solution, it aims for a satisfactory one.
A divorce of ownership and control allows the satisficing principle to occur
[diagram]
AQA Spec – Additional Content
The reasons for and the consequences of a divorce of ownership from control
- Principle Agent Problem – agent is inclined to act in their own interest which may cause conflict regarding which business objectives to prioritise
- ‘Shareholder Activism’- shareholders gain more control over the decisions of the firm when a manager sells their shares, potentially putting pressure on the management of the firm
- Owners of the firms lose some of their control when they sell their shares, which could result in conflicting objectives between the different stakeholders in the firm
Other business objectives
- Growth
- Survival
- Increasing their market share
- Environmental
- Ethical
- Quality of products
- Worker welfare
OCR Spec – Additional Content
Sales Volume Maximisation
A firm aims to sell as much of their products as they can, without enduring a loss. This is where Average Cost = Average Revenue
Firms may perform Sales Volume Maximisation to gain a larger market share
Growth Maximisation
Firms may choose to increase the size of their firm and expand – they could do this to take advantage of economies of scale
In the long run, firms will have lower costs of production which will generate greater profits
Firms can grow by merging or taking over other firms, or expanding their product range
Utility Maximisation
Firms want to generate the highest profits by prioritising consumer satisfaction and allowing them to achieve maximum utility when consuming the good / service
Social Welfare and Corporate Social Responsibility
Some firms may aim to operate more ethically to maximise social welfare, as a result of taking accountability and responsibility for the negative consequences on the environment
EDEXCEL B Spec – Additional Content
Return on Investment
Entrepreneurs engage in risk-taking by making investments, which they can earn profit from as a reward for taking the risk – this is known as the return on investment
The ROI provides indication of how profitable an investment is. An investment with a higher ROI appears as more attractive since it is likely to generate more profit.
Employee Welfare
Some firms may aim to put employee satisfaction first as it will encourage them to be more productive and do a better job.
Employee welfare also increases towards the employer, making them less likely to leave
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
1. Identify the three main business objectives (3 marks)
2. Draw a diagram for Revenue Maximisation and identify the point at which firms achieve this (4 marks)
3. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages for firms achieving Revenue Maximisation (6 marks)
4. Draw a diagram for Profit Maximisation and identify the point at which firms achieve this (4 marks)
5. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages for firms achieving Profit Maximisation (8 marks)
6. Draw a diagram for Sales Maximisation and identify the point at which firms achieve this (4 marks)
7. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages for firms achieving Sales Maximisation (6 marks)
8. Using a diagram, explain what is meant be ‘Satisficing’ (4 marks)
Next Revision Topics
A Level Economics Past Papers