Maximum Prices (Price ceilings) – Economics Revision – The Tutor Academy
Maximum Prices (Price ceilings) – Economics Revision – The Tutor Academy
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Maximum Prices (Price Ceilings)
A maximum price (Ceiling) occurs when a government sets a legal limit on the price of a good or service.
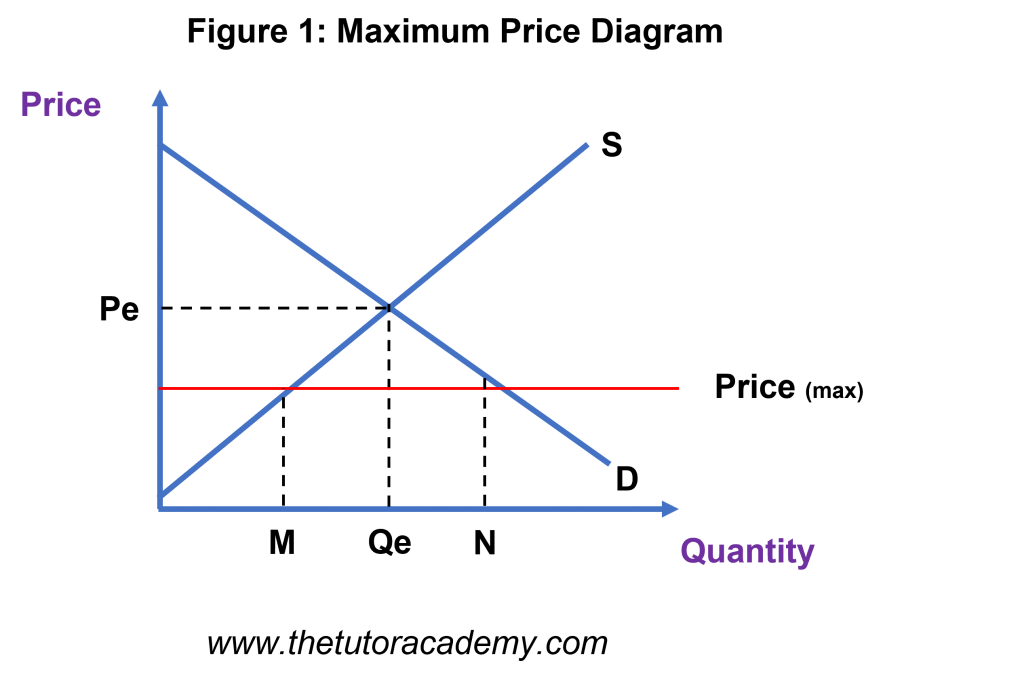
The Equilibrium Price is Pe. With the implementation of a Maximum Price below the Equilibrium Price, there will be a shortage of MN Kilos.
For example, the government may set a maximum price on bread of £1 or a maximum weekly rent that can be charged £150.
Advantages of a Maximum Price
- More affordable products – maximum prices enable families on a relatively lower income to be able to afford products
- Price Stability – they help to keep prices steady and prevent an increase in the country’s inflation rate
- Greater Demand – maximum prices mean the price is set below the equilibrium price; this encourages consumers to buy more goods / services, leading to an increase in demand
Disadvantages of a Maximum Price
- Shortages – with a maximum price, there is likely to be a shortage as the supply for the good / service will drop due to suppliers making less money from selling their products
- Lack of Incentive – lower prices may discourage firms to keep the product or increase the supply
- Black Market – the shortage of goods may lead to the existence of a Black Market where suppliers will sell their products illegally at price much higher than the maximum price
- More Unemployment – with a maximum price, firms may be likely to supply less of the product, resulting in less output and higher unemployment
- Less Choice – producers may choose to leave the market and enter a different one where they can sell their products at a more profitable price. Consumers will be left with less choice and variety
Quick Fire Questions
1. Define ‘Maximum Price’ (2 marks)
2. Using a diagram, explain the impact of a Maximum Price on the price and output of goods / services (4 marks)
3. Identify and explain three advantages of implementing a Maximum Price (6 marks)
4. Identify and explain five disadvantages of implementing a Maximum Price (10 marks)
Next Revision Topics
- Minimum Prices
- Direct & Indirect Taxes
- Government Failure
- Subsidy
- Externalities
- Merit & Demerit Goods
- Public & Private Goods
- Consumer & Producer Surplus
A Level Economics Past Papers